Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and/or purchase an item, I will receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thank you for helping me earn a little coffee money and afford to create more great content.
Benefits of Hyperconvergence for Edge Computing
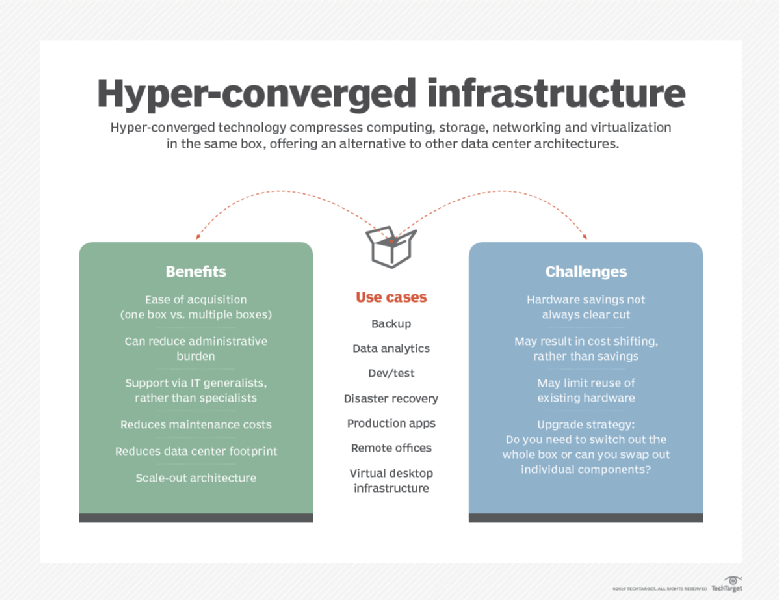
Hyperconvergence, also called Hyperconverged Infrastructure or HCI, is a technology framework that combines storage, compute, networking and hypervisor into a single solution in order to reduce complexity and increase scalability. Popular use cases for hyperconvergence are deployments that push compute infrastructure outside the traditional campus or data center, like edge computing.
Edge computing is an information technology paradigm where data is distributed from a central source to the edge of the network to be as close to the originating source as possible. With edge computing, processing power is moved closer to the end-user device in order to reduce latency and increase performance. An edge computing architecture has many smaller nodes spread across a wider geographic footprint, rather than a more traditional design where many racks of servers reside at a central data center.
As of 2020, about 10% of enterprise-generated data was created and processed using edge computing. This figure is expected to keep expanding as applications continue to become more resource and bandwidth-intensive.
Why hyperconvergence for edge computing?
Hyperconverged infrastructure collapses traditional storage, compute and network silos into a single, unified system, rather than having separate units for networking, computing, storage, virtualization, and management. Much like edge computing is replacing large, centralized silos of data, hyperconvergence is replacing large, complex storage networks, with centralized, scalable nodes.
There are numerous benefits of hyperconvergence for edge computing including:
- Smaller footprint
With HCI, all storage, compute, virtualization, and networking components are unified leading to a smaller footprint. This means that edge computing deployments can leverage small deployment footprints at data centers, thereby reducing cost for both space and power. HCI systems can be deployed at a larger number of edge locations in order to reduce latency and bring resources closer to users and applications.
- Simplified deployment
Deployment of hyperconverged infrastructure is simple because all of the components required are prepackaged and largely preconfigured. This reduces the complexity of deployment, and also reduces the amount of engineering resources required to deploy a new edge computing network point of presence. Adding additional capacity is as simple as deploying an additional node, making it easy to scale locations where additional capacity is required.
HCI software can be deployed on commodity hardware, like systems from Supermicro. They can also be purchased in prepackaged bundles such as Lenovo’s ThinkAgile series.
- Simplified management
Edge computing nodes that are deployed in a traditional fashion require server and network administrators to manage all components of the storage, server, network and hypervisor separately. The integrated and unified architecture of HCI makes it much simpler to manage on an ongoing basis. Oftentimes, management can be done at the hypervisor level, as well, further simplifying system administration of storage and virtual machines.
- Easier to scale
Using this HCI makes it easier to scale up your computing resources to support newer applications that use modern resource-intensive technologies like VDI, AI, and IoT. Hyperconverged infrastructure is ideal for edge computing nodes that may need to grow quickly as customers or resource requirements expand. Additional nodes can be added like building blocks to scale performance and capacity. The fact that hyperconverged infrastructure is pre-configured also makes scaling easier, as systems generally ship from the factory fully integrated and tested. HCI is perfect for applications that scale linearly, as deployment is as simple as adding additional nodes.
- Better user experience through reduced latency
Hyperconverged infrastructure reduces latency between server components improving performance for edge computing devices. This leads to a better experience for the end-users and improved application performance.
- Easier to maintain
The simplified and standardized architecture of hyperconvergence minimizes the time and expense of technology maintenance. Rather than having to maintain and support disparate devices from several technology manufacturers, HCI provides a single integrated nodes to support. Support services from HCI technology providers generally include both hardware and software, even when the software is from a third party provider.
Most organizations do not deploy full-time IT support for their edge computing sites or remote data centers, so using hyperconverged infrastructure at the edge means less attention and maintenance is required when compared to legacy architectures. The cost required for annual maintenance contracts is also typically reduced.
Final thoughts
Using the hyperconverged infrastructure for edge computing deployments has numerous benefits that organizations can take advantage of. Smaller footprint, simplified deployment, maintenance and management, seamless scalability, and improved performance are all reasons to consider hyperconvergence for edge computing.