The Benefits of Hyperconvergence
Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and/or purchase an item, I will receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thank you for helping me earn a little coffee money and afford to create more great content.
There is a high demand for quicker and more dependable storage performance in today’s business landscape. The faster you can collect, store, and utilize your data, the more of an advantage you possess.
With that in mind, Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) offers a way to a safe and modern infrastructure. By integrating computation, storage, and networking into a single system, HCI simplifies management, consolidates resources, and minimizes costs.
This article will look at the benefits of HCI adoption, providing a better understanding of why it is growing and why many organizations consider it vital to their strategic IT priorities.
What is Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI)?
Hyperconverged Infrastructure combines servers and storage with intelligent software to produce flexible building blocks that replace discrete servers, storage networks, and storage arrays. It mixed commodity datacenter server hardware with locally attached storage devices and distributed applications to eliminate legacy infrastructure pain points.
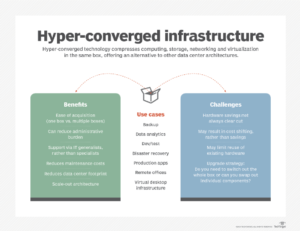
The Benefits of HCI Adoption
HCI adoption offers a plethora of benefits; some of the most notable include the following:
Backup and Replication
In an HCI scale-out infrastructure virtualized computing, networking, and storage are all integrated into a manageable infrastructure.
Typically, a hypervisor running a software-defined storage (SDS) solution gets used to cluster servers together in an HCI architecture. A virtualization layer provides shared data services for HCI systems, such as data redundancy, networking, storage, and a distributed file system.
Ultimately, production systems can be continuously replicated to the HCI configuration so that you can create virtual machines. Replica virtual machines can be brought online and hosted on hyper-converged systems in a production infrastructure failure.
HCI storage is a proven high-value architecture that boosts scalability while reducing data center management complexity. It has the potential to save money, decrease administrative strain, and simplify your working environment. HCI backup solutions can reduce or eliminate downtime by implementing rolling software upgrades across the cluster’s nodes.
Data Recovery
Many organizations embrace HCI because of its efficiency and manageability advantages. HCI providers preconfigure and add the appropriate software stack to off-the-shelf commodity components.
Most disaster recovery incidents are caused by a major loss of a data center, like a fire or flood, the loss of equipment in the data center, the failure of a single server, or problems with the network that prevent access to the network.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure, which combines storage, computer, and network hardware with hypervisor software to create and run virtual machines, works well for disaster recovery to protect against these problems.
The HCI environment can host the failed-over workload until the primary location is operational again or even permanently if necessary.
Costs
HCI provides on-premises systems with the agility and pay-as-you-go benefits of the public cloud with centralized and efficient control. Businesses can buy only the storage and computing power they need now and then easily scale up as their needs change.
Even though HCI does not replace the entire data center, industry-standard hardware and software mean a faster procurement process and fewer vendors. Cost reductions are certain because of speedier project turnaround times, more rapid deployments and recoveries, and less finger-pointing.
HCI Disaster Recovery Use Cases
The use of HCI to update infrastructure, apps, and hybrid cloud environments will continue. So, here is a list of some of the most popular HCI use cases.
Datacenter Consolidation
Server, storage, and networking systems are consolidated into a single data center for easier management by the operations team, freeing up IT resources to work on new initiatives to further its goals.
Rather than achieving more with less, this approach focuses on enhancing the end-overall user’s experience. Moreover, it is far easier to manage fewer silos when you combine your data center operations, giving you more options for capacity planning. With fewer silos, data recovery in a disaster event becomes a simpler and quicker process. This allows you to pinpoint the cause of a disaster and get back up and running as quickly as possible.
In the end, HCI can give you the ability to easily add nodes, allowing you to accommodate an ever-expanding workload and scalability without sacrificing dependability in a disaster event.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
Desktops as a Service (DaaS) and Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) are two techniques enterprises use to bring order to desktop chaos. CIOs and desktop architects struggled with VDI installations and frequently gave up on the technology’s potential when scientists introduced HCI to the market. Often, poor storage performance and architectural complexity result in VDI failure.
HCI condensed the complex components of VDI into a single device, frequently set with just enough flash storage to enable enterprises to weather the boot and login storms that plagued earlier initiatives. HCI expands as your needs grow, allowing you to add more nodes to your infrastructure, increasing performance, and enabling your storage system to complete more work in less time.
Greater scalability implies the capacity to manage the exponential growth of data generated by the Internet of Things (IoT), movies, images, files, and applications. The ability to add more storage capacity to your system adds value to managing your different workloads and assures that your infrastructure can accommodate future data demands.
Edge Computing
Computing operations outside an organization’s data centers and cloud settings get referred to as edge computing. HCI is an excellent fit for the classic remote office/branch office (ROBO) architecture because hyper-converged clusters are frequently fairly small. Even the largest businesses have minimal requirements in the periphery. Thus, an HCI implementation must scale down to support these situations.
Furthermore, this is one use case in which simplicity and ease of use are critical. Because many edge environments lack specialized IT employees, the infrastructure deployed in those locations must be rock-solid and simple to manage. It should also be scalable and simple to develop if a store or office expands and requires more workload capacity.
The requirements at the edge are simplicity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. HCI enables enterprises to develop a standard edge architecture and then deploy it as many times as needed to serve business demands while maintaining the capacity to scale.
Conclusion
As established, it is more critical than ever for organizations to have access to quicker and more dependable storage. As the speed of innovation and change continues to accelerate businesses forward, HCI puts IT in a better position to assist companies in reaching their objectives.
A solid option to consider for data center consolidation, edge computing or VDI is the HPE Simplicity DL380 Gen10. Built on HPE’s DL380 server series, it provides a compact form factor appropriate for edge computing, while offering expandability up to 96 nodes.